February 25
With the rise in popularity of cloud-based data storage, more people are asking where and how information is actually stored by cloud providers. More precisely, what exactly is the ‘cloud’, and how secure is storing and sending information through the virtual network? It’s important to have a basic understanding of how your information is being handled–particularly the aspects of a service provider that you should be cognizant of in order to ensure the safety and privacy of your data.
How Cloud Storage Works
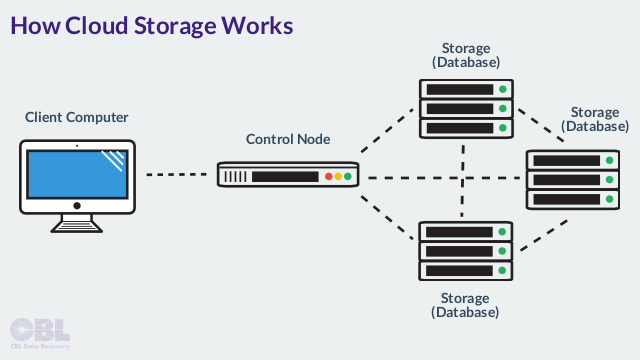
Cloud computing is a relatively new concept for the majority of consumers. Essentially, it refers to the network of computers used by companies to store and transfer users’ data as a service. A typical cloud storage system includes a master control server that connects to both the client computers (i.e. you) and usually a network of several database storage servers.
Advantages of cloud storage include being able to access your data anywhere at any time and never having to worry about running out of space on your own device. With the cloud, you aren’t forced to carry around a physical storage device with you– your data is accessible from any device and location with internet access. Furthermore, the growing amount of data in the world that is being created, shared, and stored across the internet–especially with the rise in global correspondence and networking– has made limited storage space a real concern for consumers and businesses alike. On the flipside, cloud-based storage providers simply need to network additional database servers to the master control node to resolve any growth in demand.
It’s also important to note the risks involved with cloud computing and storage. While not all providers share the same level of vulnerability, there is an inherent risk of both corruption and data loss, as well as data theft when handing your data over to a third-party. All of the data is still stored on hard drive arrays in servers that are susceptible to many of the same faults as the storage in your laptop or desktop computer. So while you may not experience the effects of data loss directly, the IT teams maintaining data centers still do and have to act accordingly.
Depending of which provider you use, the data center could be based in a different country, or possibly even a different continent. Some of the larger cloud providers have several data centers which could be spaced apart from one another across several different locations.
First off, you may be wondering why, or if, you should care about these details. Does it matter one way or the other where the data center is based? The answer is yes, it does matter–particularly if the facility is located in a country outside of your own. Physical security is just as important as network security in regards to protecting cloud-based data.
Since clients are trusting these data centers to transmit their stored data to them whenever they need access, people rely on the safety of the facility and equipment within. This has a lot of implications for the provider, including the electric wiring supporting the workload of the server network, the heating and cooling system within the facility, the physical security of the facility and servers, and the techniques used to protect people’s private data from malicious hackers and cyberattacks. Furthermore, laws and regulations for secure data protection may differ from country to country, so using a provider with foreign data centers may pose more of a risk depending on the country.
Means used by providers to secure the data stored include data encryption and authentication, i.e. requesting a user name and password to access the information. While these tactics do a pretty effective job at safeguarding sensitive information from being available to the general public, advanced hackers have in the past found ways to get around the security measures in place.
Reliability-based concerns refer to the issues that can arise if the cloud storage network is prone to technical failure or if the company isn’t in a financially stable position to keep up with advanced security measures and monitoring.
The recent uprising of cloud-based products and services has increased the prevalence of cyberattacks, identity theft, and online security breaches. Most cloud providers invest a great amount of money to measures preventing the corruption and theft of their servers and data stored within. Even so, it’s important to understand the physical and network-based threats facing virtual data storage to select the best option for keeping your private information safe and secure.
Category: data loss prevention
Tags: business continuity, business data, cloud, cloud storage, corrupted disks, data center, data security, hard drive failure, personal data, storage